Key Takeaways
Modern metal art sculptures transcend traditional forms, merging industrial materials with light manipulation to redefine spatial experiences. These works leverage metallic surfaces—from polished stainless steel to oxidized iron—to interact with ambient illumination, creating kinetic patterns that evolve throughout the day.
"Light isn’t just an accessory; it’s a collaborator. The way metal reflects or absorbs light can transform static sculptures into living entities," notes sculptor Elena Vázquez.
Key considerations include the interplay of texture and scale: brushed finishes soften light diffusion, while angular geometries cast sharp, dynamic shadows. Commissioned pieces often integrate site-specific factors, such as architectural lighting or natural sunlight paths, to amplify their visual narratives. For collectors, prioritizing artists who experiment with mixed metals (e.g., copper paired with corten steel) ensures durability alongside aesthetic innovation.
As these sculptures gain prominence in public and private spaces, their role extends beyond decoration. They act as focal points that harmonize or contrast with environments—polished installations in minimalist lobbies, for instance, amplify openness, while rust-textured pieces in gardens echo organic decay. Understanding these dynamics helps curators and designers select works that align with both functional and artistic goals.

The Evolution of Metal Sculptures in Modern Art
Metal sculptures have undergone significant transformation since their early utilitarian origins, evolving into a cornerstone of contemporary artistic expression. The 20th century marked a pivotal shift as artists like Alexander Calder and Julio González reimagined metal’s potential, moving beyond static forms to embrace abstraction and kinetic energy. Industrial advancements introduced new materials—stainless steel, aluminum, and corten steel—enabling sculptors to experiment with scale, durability, and environmental integration.
By mid-century, movements such as Minimalism and Constructivism emphasized geometric precision, stripping metal art to its essential lines and planes. This period also saw the rise of site-specific installations, where sculptures began interacting with architectural spaces and natural light. Contemporary practitioners now blend traditional forging with digital fabrication, using laser cutting and 3D modeling to create intricate, fluid designs. Notably, some artists incorporate whimsical elements, such as Cartoon sculpture, to juxtapose playfulness with industrial rigor.
Today’s metal sculptures reflect a duality of permanence and adaptability, mirroring societal shifts toward innovation while honoring craftsmanship. Their evolution continues to challenge perceptions of materiality, transforming metal from a rigid medium into a dynamic storyteller of light, space, and cultural identity.

Metal Artistry: Merging Light and Spatial Dynamics
Contemporary metal sculptors are redefining spatial experiences by engineering works that interact with light as a core design element. Using reflective alloys like polished stainless steel and brushed aluminum, these creations transform static environments through calculated light refraction. Artists such as IP character sculpture employ geometric precision to angle surfaces that cast evolving shadow patterns, turning blank walls into kinetic canvases as daylight shifts.
| Metal Type | Light Interaction | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High reflectivity, sharp shadows | Large public installations |
| Corten Steel | Diffused rust-toned glow | Outdoor architectural accents |
| Aluminum | Soft directional reflection | Ceiling-mounted pieces |
This synergy between material science and optics enables site-specific works to visually expand confined areas. A helical steel structure in a corporate atrium, for instance, might compress shadows at noon before stretching them dramatically by dusk. Such intentional light manipulation requires 3D modeling to predict how angles and curves will behave under varying illumination. Commissioned pieces increasingly incorporate LED systems to maintain dynamic interplay after dark, blurring boundaries between sculpture and functional lighting design.
Commissioned Metal Works for Contemporary Spaces
Commissioned metal art sculptures have become pivotal in redefining architectural environments, merging artistic vision with functional design. These bespoke creations often serve as focal points in corporate lobbies, public plazas, and luxury residences, where artists collaborate closely with architects and designers to align with spatial aesthetics. By integrating materials like brushed stainless steel, oxidized copper, or corten—known for its weathered patina—artists manipulate metallic surfaces to interact with ambient light. For instance, perforated panels or layered structures cast evolving shadow patterns that shift with daylight, creating a kinetic sculpture-like effect without mechanical motion.
Such works balance geometric precision and organic fluidity, responding to the scale and purpose of their settings. A corporate installation might emphasize angular forms to echo institutional stability, while a residential piece could incorporate curved, tactile elements to evoke warmth. Beyond aesthetics, these sculptures often address acoustic or spatial division needs, proving that metal’s versatility extends beyond visual impact. As daylight fades, embedded LED systems or strategic spotlighting amplify textural contrasts, ensuring the artwork remains dynamic across varying conditions. This tailored approach transforms metal from static material into a medium that actively shapes human interaction with space.
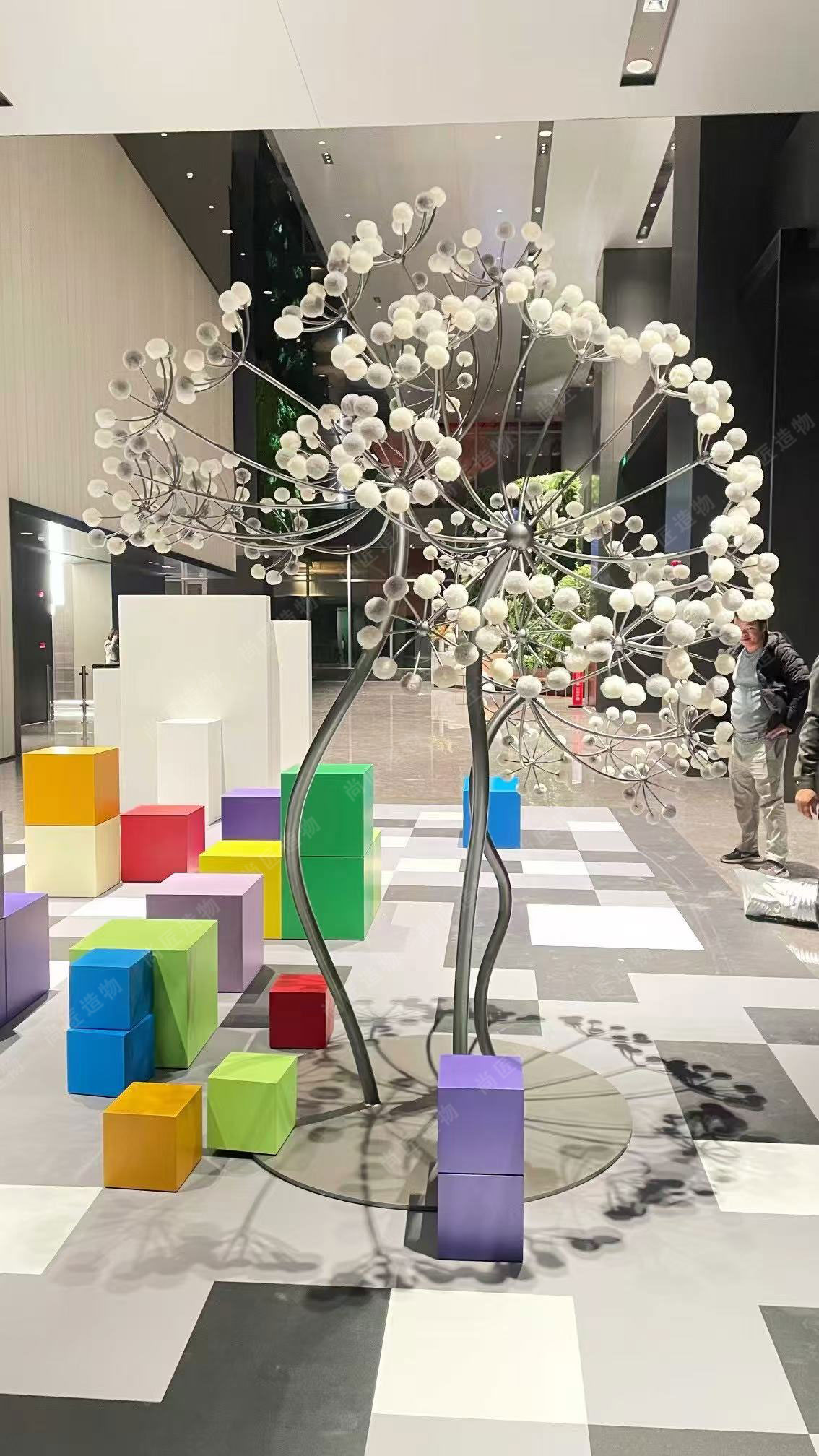

Dynamic Textures in Modern Metallic Sculptures
Contemporary artists harness advanced metalworking techniques to create surfaces that interact with environmental conditions. By manipulating stainless steel, bronze, and aluminum through processes like acid etching, heat oxidation, and precision laser cutting, they produce textures that shift in appearance under changing light angles. These dynamic surfaces transform static sculptures into kinetic experiences—rippled patterns catch sunlight differently at dawn versus dusk, while brushed finishes scatter artificial illumination in urban settings.
A notable example includes stainless steel sculpture installations that employ mirrored finishes to reflect and distort surrounding architecture. This interplay between material and environment allows sculptures to "converse" with their spatial context, amplifying depth and movement. Commissioned works often integrate these textural elements to complement specific sites, such as corporate lobbies where geometric patterns echo structural motifs. The result is a tactile dimensionality that invites viewers to observe how light and surface collaborate to redefine perceptions of form and space.

Shadows and Light: Metal Sculptures’ Visual Impact
Modern metal art sculptures transform static spaces into dynamic environments by manipulating light and shadow. Artists strategically employ reflective surfaces, perforated designs, and angular geometries to choreograph how illumination interacts with metallic forms. Polished stainless steel captures ambient light, casting sharp, geometric shadows that shift with the sun’s trajectory, while oxidized iron surfaces absorb brightness, creating softer, diffused silhouettes. This interplay becomes particularly pronounced in Realistic sculpture commissions, where textured metals like brushed aluminum or hammered copper introduce layered dimensionality to shadow patterns.
Spatial context further amplifies these effects. Suspended installations in atriums leverage overhead lighting to project intricate shadow lattices onto floors, whereas wall-mounted pieces use directional spotlights to emphasize depth through contrasting chiaroscuro. Contemporary sculptors often experiment with mixed-media elements—such as translucent resins or glass fragments embedded in metal matrices—to fracture light into prismatic displays. Such techniques not only redefine physical spaces but also evoke emotional responses, as viewers experience the artwork’s evolving character under changing lighting conditions. This symbiotic relationship between materiality and illumination underscores metal sculpture’s unique capacity to animate architectural environments.

Curating Immersive Metal Art Installations
Curating modern metal sculptures for immersive installations requires balancing material properties with environmental storytelling. Designers analyze spatial dimensions, lighting conditions, and audience pathways to position works where metallic surfaces interact dynamically with natural or artificial light. For example, reflective stainless steel panels might anchor a sunlit atrium, casting prismatic shadows that evolve with daylight angles, while oxidized copper pieces in dimmer corridors could amplify ambient warmth through strategic LED placements.
The integration of complementary mediums, such as Fiberglass sculpture, often enhances textural contrast—smooth polymer finishes juxtaposed against hammered steel create tactile dialogues. Site-specific commissions frequently involve computational modeling to predict shadow patterns or reflectance intensities, ensuring artworks adapt to seasonal light shifts. Curators also prioritize viewer engagement, positioning sculptures at heights or angles that invite interaction without compromising structural integrity. By harmonizing metallurgical science with artistic intent, these installations transform static spaces into kinetic experiences where light, form, and movement coalesce.
Innovative Techniques in Metal Sculpture Crafting
Contemporary metal sculptors are redefining traditional methods through technological integration and material experimentation. Advanced tools like 3D modeling software allow artists to simulate light interactions and spatial relationships before fabrication, ensuring precise alignment with architectural environments. Laser-cutting systems and CNC machining enable intricate geometric patterns, while plasma arc welding creates seamless joins in large-scale installations.
A growing emphasis on sustainability has led to innovations in metal recycling and patina development. Artists now employ electrochemical processes to accelerate oxidation, producing controlled color variations that respond uniquely to ambient lighting. Hybrid approaches, such as combining forged steel with translucent resin inserts, introduce layered dimensionality. These methods not only enhance metallic textures but also amplify how sculptures interact with shifting natural and artificial light sources.
The field continues to evolve through collaborations between sculptors, engineers, and architects. Kinetic mechanisms powered by solar energy or motion sensors add dynamic movement, transforming static metal forms into evolving spatial compositions. Such technical advancements ensure modern metal art remains adaptable to both private collections and public installations, bridging artistic vision with functional design.

Metal Art for Transforming Architectural Ambiance
Architects and designers increasingly integrate modern metal sculptures to redefine the atmosphere of built environments. Unlike traditional decor, these works interact dynamically with their surroundings—reflecting light, amplifying spatial proportions, and altering perceptions of depth. For instance, polished stainless steel installations in lobbies can mirror natural light patterns, creating illusions of expanded space. Conversely, oxidized copper pieces in courtyards absorb ambient brightness, fostering contemplative moods through muted, earthy tones.
Commissioned metal artworks often serve as focal points that harmonize with structural elements like glass facades or concrete walls. Artists collaborate with design teams to align textures and forms with architectural intent—a ribbed aluminum panel might echo a building’s angular roofline, while a perforated bronze screen filters sunlight into geometric patterns across floors. This synergy between art and architecture transforms static spaces into evolving experiences, where shifting daylight and viewer perspectives reveal new details. Such installations not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also deepen the emotional resonance of environments, proving metal’s versatility as both medium and mediator in spatial storytelling.
Conclusion
Modern metal art sculptures continue to redefine how we experience physical spaces, merging industrial materials with the ephemeral qualities of light and shadow. As explored throughout this article, these works transcend traditional artistic boundaries, acting as both standalone pieces and dynamic collaborators with their environments. From commissioned installations in urban plazas to intimate gallery displays, the interplay of metallic textures and shifting illumination creates narratives that evolve with time and perspective.
The integration of innovative techniques—such as laser-cut patterning, oxidized finishes, and kinetic elements—ensures each sculpture responds uniquely to its surroundings. This adaptability not only enhances architectural ambiance but also invites viewers to engage with art beyond passive observation. By balancing structural permanence with transient visual effects, modern metal sculptures exemplify how contemporary art bridges functionality and imagination, leaving lasting impressions that reshape our relationship with space.
FAQs
What materials are commonly used in modern metal sculptures?
Artists typically work with stainless steel, corten steel, and aluminum for their durability and ability to interact with light. These metals are often treated with patinas or polished finishes to enhance visual depth.
How do metal sculptures interact with light in indoor spaces?
Textured surfaces and perforated designs catch ambient or directed lighting, casting intricate shadows that evolve throughout the day. This dynamic interplay transforms static pieces into time-based installations.
Can commissioned metal artworks withstand outdoor environments?
Yes, weather-resistant metals like corten steel are widely used for outdoor installations. Protective coatings and structural engineering ensure longevity while maintaining aesthetic integrity against elements.
What factors influence the placement of large-scale metal sculptures?
Curators consider spatial dimensions, sightlines, and light sources to optimize visual impact. Reflective surfaces may be positioned to frame architectural features or amplify natural illumination patterns.
How are modern metal sculptures maintained over time?
Routine cleaning with non-abrasive solutions preserves finishes, while inspections address oxidation or structural stress. Indoor pieces require minimal upkeep compared to outdoor installations exposed to weathering.
Do metal sculptures integrate with digital lighting systems?
Many contemporary artists incorporate programmable LED arrays to create synchronized light patterns, merging traditional metalworking with interactive technology for site-specific installations.
 ch
ch English
English